API Gateway Architecture
In this microlearning, we’ll explore key architectural considerations for setting up API Gateways within eMagiz. We'll cover the basic concepts of single-lane and double-lane setups, which refer to the number of runtimes used and their role in ensuring system reliability. Additionally, we'll look at different architecture configurations, including how to position runtimes in the Cloud and on-premises environments, and the memory requirements for these setups. Understanding these aspects will help you design a robust and efficient API Gateway architecture.
Should you have any questions, please contact academy@emagiz.com.
1. Prerequisites
- Intermediate knowledge of the eMagiz platform
- Good working experience in the Design phase Architecture and Deploy Architecture
- Created several API gateway integrations
2. Key concepts
- Single lane -> Single runtime per types
- Double lane -> Two or more runtime per type to handle failover setups
3. Architecture considerations
3.1 Architecture components API Gateway
The following picture displays a general architecture of the API Gateway. This picture has been taken from the eMagiz Design Architecture section as that illustrates the below key points.
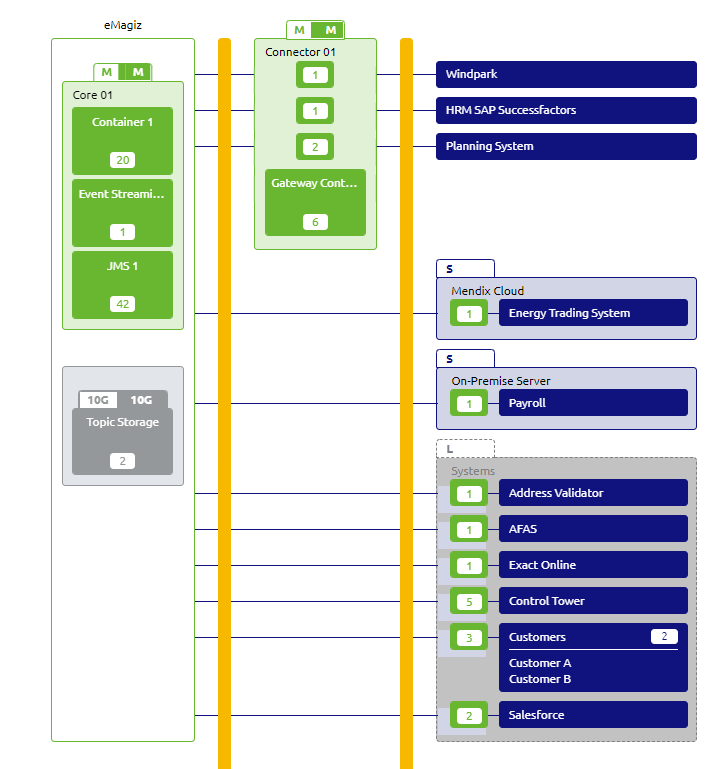
Key notes
- Gateway runtime
- The Gateway has a separate runtime where the associated gateway flows are deployed in. The exit gates and all entry flow are the typical flow types present in this runtime, next to the usual infrastructure flow
- Location runtime
- The Gateway runtime is located in a Cloud machine, and is specifically put on the Connector machine. The Connector machine has the ability to allow incoming data (secured) traffic from outside the Virtual Private Cloud that each client has. The Core machine does not have this option due to security reasons. The eMagiz Cloud handles the proper and secure routing to the API gateway.
- Gateway only runtime
- These are system that act as application user of 1 or more operations made available in the API Gateway. In case the system is only connected in the Design phase as such an application user, than that system only acts as input for User Management. The system doesn't need to be deployed as a runtime on the Connector machine, and should therefore be placed on an excluded machine. In the picture above, Exact online is such a system.
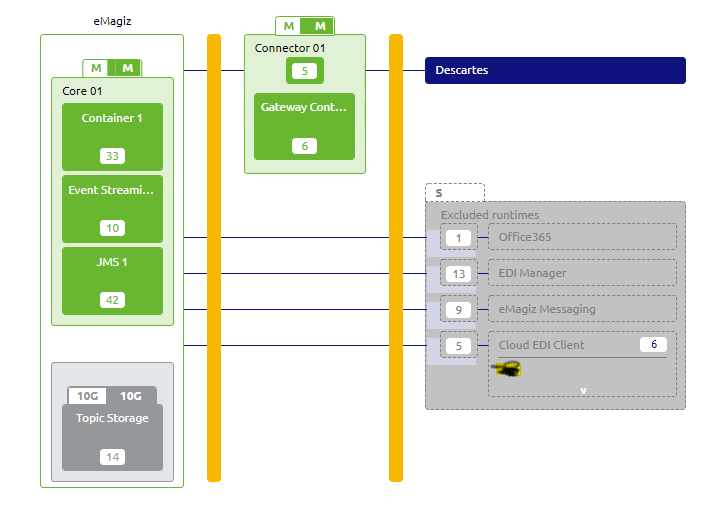
3.2 Single lane Cloud setup
Single lane setup in eMagiz means that all runtimes are provided once in the architecture diagram * there is no failover or clustered approach for the runtimes. For the API Gateway, this means that you have the following machines available. In this example, you have the messaging patterns components as well with the objective to see such cases as well.
- Core 01 -> holds the JMS Server and the messaging process container
- Connnector 01 -> holds the API Gateway container and the messaging runtimes
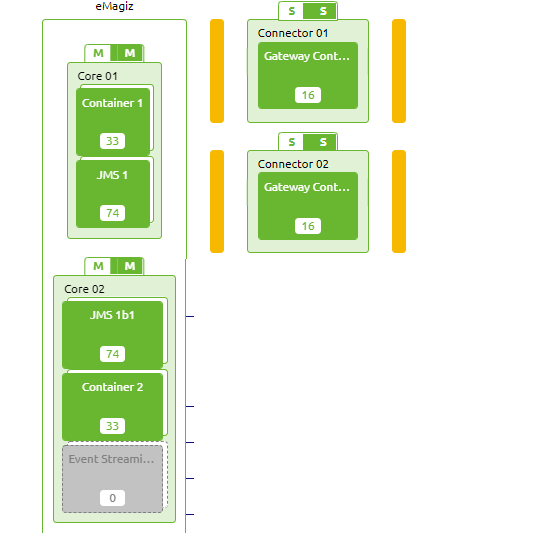
3.3 Double lane Cloud setup
Double lane setup in eMagiz means that all runtimes are provided at least twice in the architecture diagram * there is a failover for the JMS runtimes and gateway containers. For the API Gateway, this means that you have the following machines available. In this case you need to make sure that the flows are duplicated properly across the containers in Deploy * Containers. By default eMagiz will spread all flows over both gateway containers.
- Core 01 -> holds the JMS Server and the 1st messaging process container
- Core 02 -> holds the backup JMS Server and the 2nd messaging process container
- Connnector 01 -> holds the 1st API Gateway container
- Connnector 02 -> holds the 2nd API Gateway container
The choice to create a double lane API gateway is to be done where there is a requirement for very high performance around response times and throughput. Please contact eMagiz to discuss such options.
3.4 Hybrid Cloud setup
In the microlearning you can find the reasons and configuration for running the exit gates in on-premises runtimes. A view of such a architecture is displayed here:
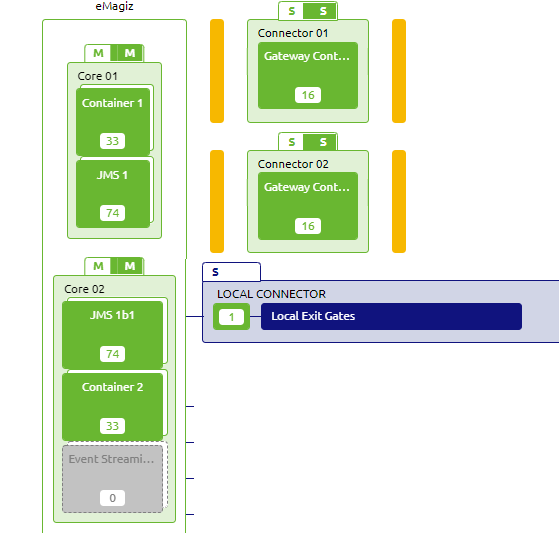
3.5 Memory
For now the memory requirements for API Gateway are the same as for Messaging flows. Please refer to the microlearning.
4. Key takeaways
- API Gateways can be part of a hybrid landscape that combines the available integration patterns.
- A single lane setup is usually sufficient for most cases.
- Hybrid setups are possbible but please be sure the ask the right questions before implementing such.
5. Suggested Additional Readings
If you are interested in this topic and want more information on it please read the help text provided by eMagiz and read the following links:
