Using eMagiz as producer
In this microlearning, we will explore how to effectively use eMagiz as a producer in the context of Event Streaming. We will guide you through the process of setting up eMagiz to produce data on specific topics, which other systems can then process in a manner they desire.
Should you have any questions, please contact academy@emagiz.com.
1. Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of the eMagiz platform
- Kafka cluster you can use to test against.
- Event streaming license activated
2. Key concepts
This microlearning centers around using eMagiz as a producer.
- By using, in this context, we mean: Being able to produce data on topics that are managed within an external Kafka Cluster, such as the eMagiz Kafka Cluster running on DSH.
- By knowing how you can easily use eMagiz as a producer in these situations, you can create event processors or create hybrid configurations (e.g., messaging to event streaming combination).
In this microlearning, we will focus on the components in eMagiz that you need to produce data on a specific topic.
3. Using eMagiz as producer
When integrating several systems, it can quickly happen that a subset of those systems can only be reached via more traditional patterns. In contrast, others can write and/or read data directly on a topic. In this microlearning, we will focus on the scenario where a component within an eMagiz flow writes data to a topic. External parties will, in turn, consume data from the topic and use it within their application context.
To make this work, you need to identify the producing system (eMagiz), the consuming system, and create a messaging offramp that ensures the messaging pattern is followed from the legacy systems to the topic. In the picture shown below, we have illustrated this in the Capture phase of eMagiz.
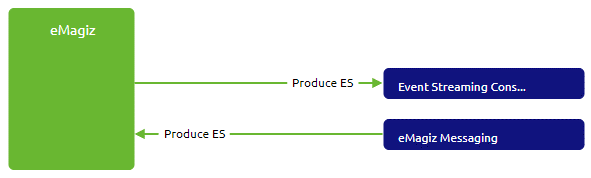
To complete the picture, we need to ensure that the data is received from a legacy system. Something along these lines:
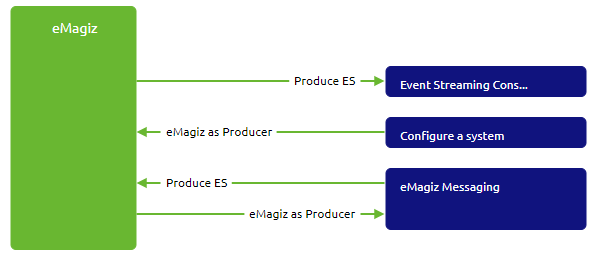
In the Design phase, you can configure your integration as explained in various of our previous microlearnings. Therefore, we will assume that you have designed your integration as intended.
3.1 View solution in Create
The first step after adding the integrations to Create is to see how eMagiz represents this depiction of reality in the Create phase. See below for the result of the Event Streaming part and the Messaging part:


As learned in previous microlearnings The Event Streaming part, in this case, automatically creates the topic by eMagiz. We will zoom in on how you can set up your messaging exit flow to produce data on the topic automatically created by eMagiz.
3.2 Produce data
When you open your exit flow, you will see that eMagiz has autogenerated some components for you.
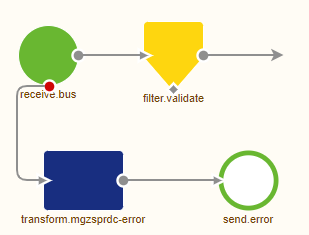
Now we need to ensure that we can produce data on the topic using the eMagiz components available in the eMagiz flow designer. In this case, we will need the Kafka outbound channel adapter.
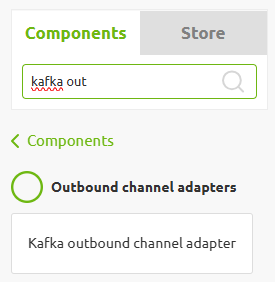
As the name suggests, this component can push data to a Kafka topic. Secondly, we need a support object that will establish the connection between the eMagiz flow and the eMagiz Event Streaming cluster, which hosts the topic. This component is called the eMagiz Data Streams Template.
3.3 Configure the support object
In this section, we will discuss all configuration options for the necessary support object.
3.3.1 Bootstrap server URL
Within this component, you need to fill in several information elements. The first element is the bootstrap server URL. The bootstrap server URL is registered via a standard property that is built up as follows: ${emagiz.dsh.bootstrapservers}.
3.3.2 Client ID
Alongside the bootstrap server URL, you will need to specify the client ID. This client ID should be built up in the following manner: {technical name system}.{technical name flow}.{technical name flow type}.${emagiz.model}.${emagiz.container}.
3.3.3 SSL Configuration
Last but not least, on the Basic tab, you need to specify the SSL-related information that allows your eMagiz flow to authenticate itself with the DSH broker. These settings need to be filled in as illustrated in the picture below. Notice that all relevant information is stored in auto-generated properties for you. These properties are as follows.
- ${emagiz.dsh.keystore.certificate}
- ${emagiz.dsh.keystore.key}
- ${emagiz.dsh.keystore.password}
- ${emagiz.dsh.truststore.certificate}
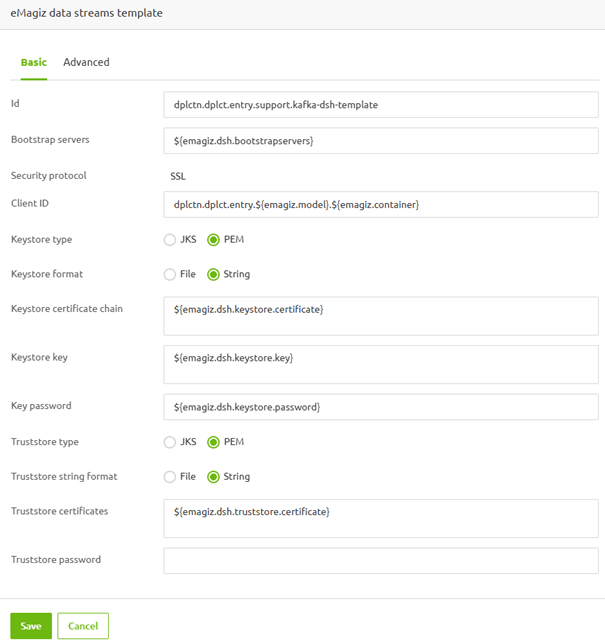
3.4 Configure the outbound component
Now that we have the support object configured, it's time to examine the outbound component. Here, we need to link the template we just created as a support object to the outbound component and define the topic to which we want to produce it. The topic name is particular in nature and therefore needs to be matched correctly. Most is auto-generated by eMagiz once more. The only thing you should alter here is the topic name, which is "two" in this example.
Once you have configured both, you end up with the following configuration for your outbound component.
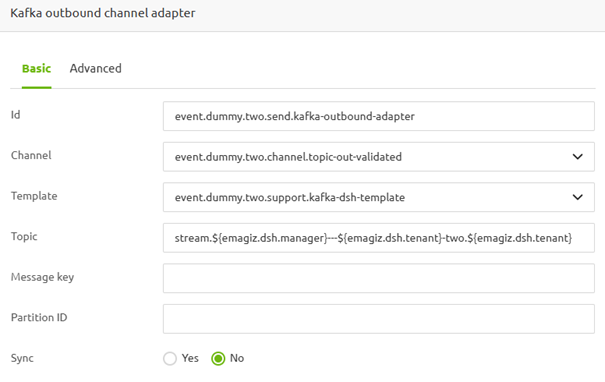
With this configured, your flow is ready to produce data on the topic. As a result, after saving, your flow should look similar to what is shown below:
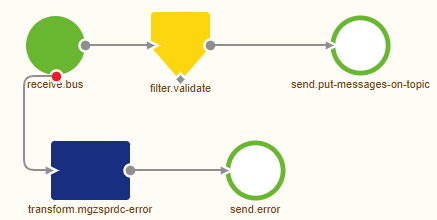
4. Key takeaways
- Utilizing eMagiz as a producer is instrumental in hybrid scenarios where you need to integrate traditional messaging patterns with event streaming.
- In many straightforward cases, eMagiz automates the data production process for you, reducing manual configuration.
- You can use the copy and paste functionality of eMagiz to give you a head start, reducing manual configuration
- A lot of auto-generated properties of eMagiz are necessary to set up the connection correctly, so ensure that you use the correct property placeholders.
- Ensure your eMagiz flow is correctly connected to the eMagiz Event Streaming cluster and configured with the necessary SSL connections to enable smooth data production.
5. Suggested Additional Readings
If you are interested in this topic and want more information on it, please see the following links:
