FTP Connectivity
In scenarios where direct communication with a local file directory is not possible or when an external party requires file placement elsewhere, FTP (File Transfer Protocol) becomes essential. This microlearning will guide you through the basics of FTP and demonstrate how to establish a connection between eMagiz and an FTP server. We will cover the prerequisites, key concepts, and best practices to ensure smooth and efficient file transfers.
Should you have any questions, please get in touch with academy@emagiz.com.
1. Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of the eMagiz platform
- Novice course on File-based connectivity
2. Key concepts
This microlearning is about FTP (connectivity).
- By FTP connectivity, we mean: Making sure that eMagiz can communicate with the FTP to exchange file-based data.
3. FTP Connectivity
In some situations, direct communication with a local file directory is not possible, or in other case, an external party requires the files to be placed elsewhere. Mainly the somewhere else is either an FTP or an SFTP. This microlearning will look at the FTP and learn how to set up the connection between eMagiz and the FTP.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a network protocol for transmitting files between computers over Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connections.
- In an FTP transaction, the end user's computer is typically called the localhost. The second computer involved in FTP is a remote host, which is usually a server.
- Servers must be set up to run FTP services, and the client must have FTP software installed to access these services.
- eMagiz provides several components to set up the FTP connection
So, where the file pickup component searches on the local host for the correct directory, the idea of the FTP setup is that the directory with whom to communicate exists on a remote host. The local host and the remote host can talk to each other via the FTP protocol. That is, in a nutshell, the difference between setting up an FTP connection and communicating with local directories.
eMagiz provides two support objects to connect to an FTP:
- Default FTP caching session factory
- Default FTP session factory
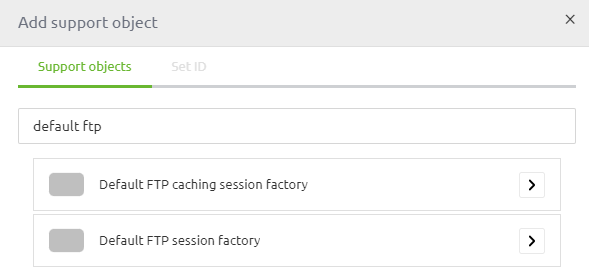
The main difference between the two is the caching part. The caching session factory comes with the option to re-use the existing session for multiple requests. In other words, this way, you do not have to authenticate yourself every time you want to communicate with the FTP. This behavior is beneficial if a high frequency of communication is needed between eMagiz and the FTP to handle the incoming and outgoing data packages.
If you only initiate communication infrequently, for example, once per day, the default session factory becomes more interesting as this closes the session after each transmission. This behavior is beneficial in cases of low-frequency communication because otherwise, the session would remain active for an extensive period.

3.1 Best practices for using FTP
3.1.1 Which session factory do I need?
When occasionally retrieving or writing files to FTP, use the _Default FTP session factory_. A new connection will be set up when you use the _Default FTP session factory_ for every message/file. On some FTP servers, this might take up to seconds for each login. This fact might impact the performance of your flow.
When you need better performance (say writing multiple files in a minute or retrieving files every minute), use the _Default FTP caching session factory_. The _Default FTP caching session factory_ shares FTP sessions for messages in your flow.
3.1.2 Do I have to set up a retry mechanism?
When writing files to FTP, it is advisable to set a retry mechanism. Find the advanced tab on your _FTP outbound channel adapter_. Under _Request handler advice chain_ add a _Retry Advice_.
3.1.3 I get a _Failed to list files/items_ or a _Failed to obtain pooled item_. What can I do?
Incorrect connection settings can cause this. Check whether the correct properties have been set and whether the runtime has retrieved the latest properties.
3.1.4 I get a _Failed to list files / items_, a _Pipe closed_ or an _input stream is closed_. What can I do?
A closed FTP session can cause these notifications due to inactivity. For the _Default FTP caching session factory_, always set the _Server alive interval_ property to 30000 (ms).
3.1.6 I get a _Failed to write to_. What can I do?
Maybe the target folder does not exist, and the _Auto-create directory_ is off. It is also possible that the connection settings are incorrect. Check whether the correct properties have been set and whether the runtime has retrieved the latest properties.
3.1.7 I often get 'Disconnecting from sftp.example.com port 22' and then a 'Caught an exception, leaving main loop due to Socket closed' warnings.
Too many connections can cause this to the same server at the same time. If you have many flows connecting to the same FTP server, ensure that the crons do not trigger simultaneously.
3.1.8 I get a 'Failed to create SFTPClient'
SFTP, FTP, and FTPS are three different remote file transfer protocols with their _session factory_ components in the eMagiz flow designer. Make sure you use the one that corresponds to the server's protocol.
3.1.9 One of my remote files is not picked up from the SFTP server (without any warning)
The default local filter is _AcceptOnceFileListFilter_. This can be replaced by your file list filter on the _FTP inbound channel adapter's_.
If every day you retrieve a file with the same filename and the _Delete remote files_ property is set, it is advised to use a different local filename. You can add the current timestamp, for example.
3.1.10 Which mode is needed
When running in the current-generation architecture (G3) the FTP always needs to run passive mode.
3.2 Configuration in eMagiz
To configure the connection between eMagiz and the FTP, we need two (or three) components. This depends on whether we want to read, write or do both while communicating with the FTP. If we're going to do both, we need both of the functional components. In all other scenarios, you only need one of the functional components. The functional components that you might need are called:
- FTP Inbound Channel adapter
- FTP Outbound Channel adapter
On top of that, you need one of the following support objects. If you are unsure of which to use, please check out the information above in this microlearning.
- Default FTP caching session factory
- Default FTP session factory
In this microlearning, we will use the FTP Inbound channel adapter combined with the Default FTP session factory to illustrate the configuration. Please note that any other combination works similarly. To configure the connection with the FTP, we first navigate to the Create phase of eMagiz. Here we open the flow we want to edit. In this example, that will be an entry flow as we want to retrieve (read) data from the FTP.
When you have opened the flow, you need to enter "Start Editing" mode. After you have done so, we first add the support object to our flow. In this case, we will use the Default FTP session factory.
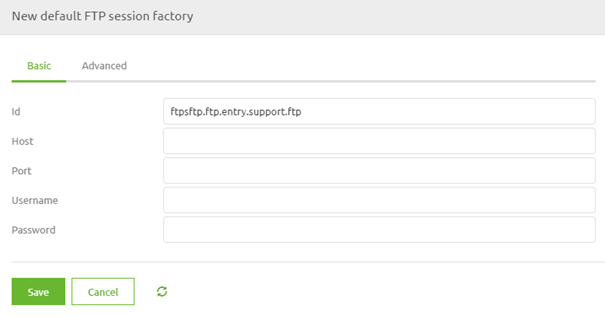
Here, we need to define at least the host and the port. Note that the username and password are optional for an FTP, which makes it less secure. Although in practice, we generally see that the FTP is secured with the help of a username-password combination. As a best practice, we use property references to fill in the various elements.
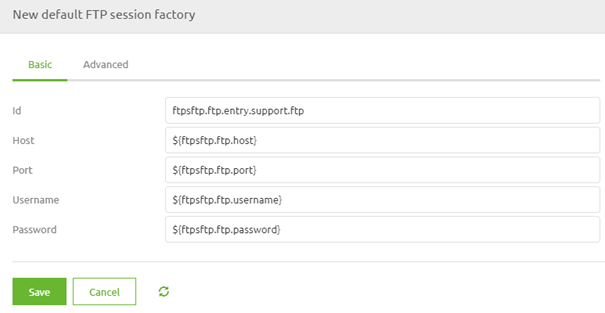
The settings on the Advanced tab don't have to be changed in most cases. If your specific setup does require a change to these settings, please consult the help texts on the component level for advice.
Now that we have configured the support object adding the FTP inbound channel adapter to the flow has become time.
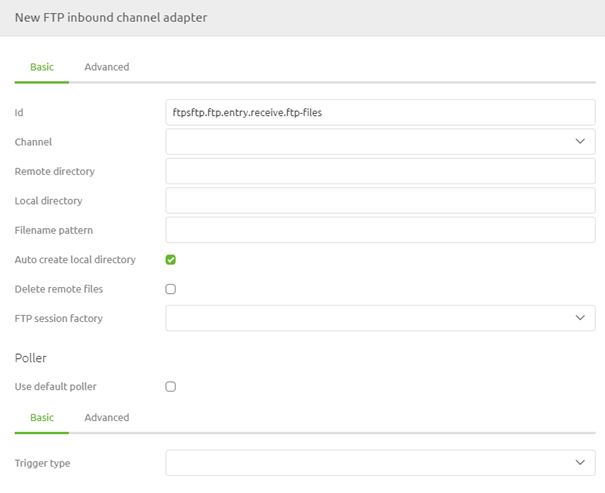
In this component, we need to define the remote directory where the original files are located. We need to specify the local directory used to store the files before they are processed temporarily. Furthermore, we need to link the support object we have just created and define a poller. For that last one, the best practice is the use of a cron trigger.
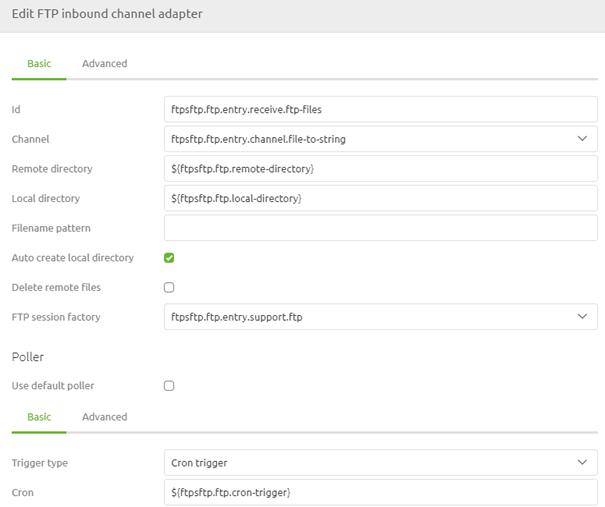
Apart from these configurations, you could also add a filter, just as we learned in the Crash Course Messaging on file-based connectivity. Finishing things off, we should consider the delete behavior we will use. Based on the filter and the business requirements, when to delete and whether to delete or not could differ. So please consider all your options in that regard.
3.3 FTP Gateway
The FTP Gateway is an additional component that can be used to interact with your FTP share. It allows the use of a set of pre-configured commands to perform actions such as deleting files. Compared to the outbound channel adapter replies are send back to eMagiz. These reply messages depend on the selected command. Every command option is explained in detail within the helptext. An example configuration to send files is shown below.
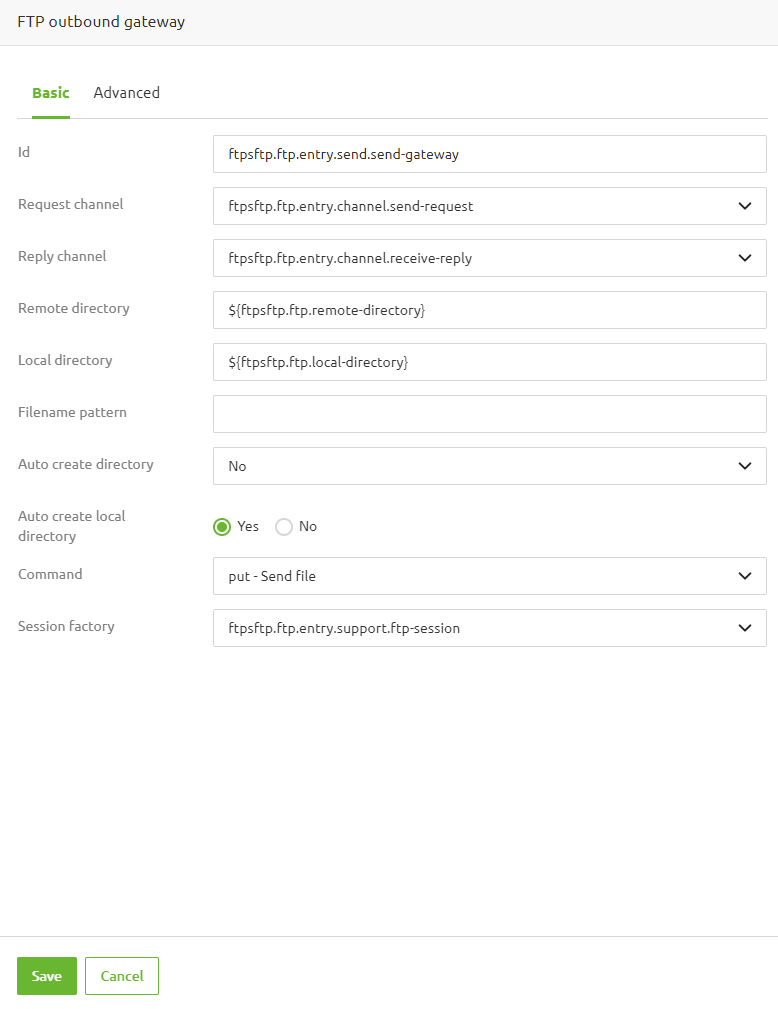
All available options are:
- List files
- List file names
- Retrieve file
- Retrieve multiple files
- Remove file(s)
- Move/rename file
- Send file
- Send mulitple files
This concludes our microlearning, in which we learned how to set up the connectivity with an FTP.
4. Key takeaways
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a network protocol designed for transferring files between computers over TCP/IP connections. It involves a local host (the end user’s computer) and a remote host (typically a server).
- In an FTP transaction, your computer is typically referred to as the localhost, while the server you're connecting to is known as the remote host. This setup facilitates secure communication between these two entities.
- For successful FTP communication, servers must have FTP services enabled, and clients must use FTP software. eMagiz offers components to facilitate this connection.
- eMagiz provides tools like the Default FTP session factory and Default FTP caching session factory to set up FTP connections. The choice between these depends on the frequency and nature of the file transfers.
5. Suggested Additional Readings
If you are interested in this topic and want more information, please read the release notes provided by eMagiz. Furthermore, check out these links:
- 1. Prerequisites
- 2. Key concepts
- 3. FTP Connectivity
- 3.1 Best practices for using FTP
- 3.1.1 Which session factory do I need?
- 3.1.2 Do I have to set up a retry mechanism?
- 3.1.3 I get a _Failed to list files/items_ or a _Failed to obtain pooled item_. What can I do?
- 3.1.4 I get a _Failed to list files / items_, a _Pipe closed_ or an _input stream is closed_. What can I do?
- 3.1.6 I get a _Failed to write to_. What can I do?
- 3.1.7 I often get 'Disconnecting from sftp.example.com port 22' and then a 'Caught an exception, leaving main loop due to Socket closed' warnings.
- 3.1.8 I get a 'Failed to create SFTPClient'
- 3.1.9 One of my remote files is not picked up from the SFTP server (without any warning)
- 3.1.10 Which mode is needed
- 3.2 Configuration in eMagiz
- 3.3 FTP Gateway
- 3.1 Best practices for using FTP
- 4. Key takeaways
- 5. Suggested Additional Readings
