H2 Database, Function
When you create a new entry in eMagiz, you might notice that the H2 database component is automatically included. This can sometimes lead to confusion about its role and purpose. In this microlearning, we will clarify what the H2 database does and why it's an essential part of every new entry. We will break down its functions, including how it temporarily stores data, acts as a bridge between the entry and the queue, and helps manage data flow.
Should you have any questions, please contact academy@emagiz.com.
1. Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of the eMagiz platform
2. Key concepts
This microlearning centers on the function of the H2 Database.
- With H2 Database we mean: A database structured that can be created and used with the help of eMagiz components.
The focal point of this microlearning will be to figure out why the H2 database is part of any auto-generated entry. The key aspects are:
- H2 Database temporarily stores data.
- Acts as a bridge between the entry (where data arrives or is retrieved) and the first queue (the onramp).
- Holds data in case the queue (the onramp) cannot be reached.
- Smoothen the amount of data that is transported from the connector to the container runtime as it periodically checks for new data.
3. H2 Database, Function
When you utilize the messaging platform you are bound to see this component automatically appear in all your entries when you create those entries for the first time. However, we see that there is quite some confusion on what the function of this component is in the entry. In this microlearning, we will try our best to explain that function to you. In another microlearning, further down the road, we will discuss other applications of the H2 database.
As you probably noticed by now is that every time you create a new entry in eMagiz some components are automatically generated for you.
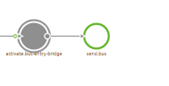
A subset of these components creates the desired H2 database including structure to receive and process messages. Those components are highlighted in the picture below.
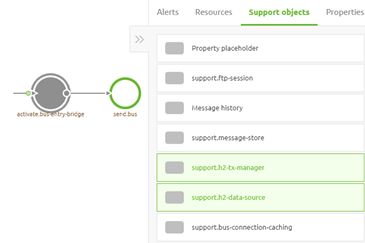
The support objects ensure that the H2 database is created and that the data in it is encrypted. Furthermore, they make sure that the database is stored in the proper location and has the correct structure. All of this is nothing you as a user should worry about. Those support objects are created with the best possible settings.
Another part of the flow is the grey circle that will become part of your main flow. This component is called a message bridge. With the help of the message bridge, you can link up certain channels to throttle messages and make sure that the endpoint (in this case the queue) does not have to do the polling on the database to check for new messages. The default setting for this component is that every 500 milliseconds 10 messages are picked up. Based on desired throughput and volume you could tweak those settings to best suit your needs. Do be aware that you should not randomly start tweaking settings.
Furthermore, this message bridge is linked to a support object (transaction manager). This configuration allows the poller action to be part of the transaction and therefore gives the ability to perform a rollback in case of error. This is crucial when you want to guarantee message delivery. If you would not have something like this and for whatever reason, the connection between the entry and the queue (the onramp) is gone messages will be lost.
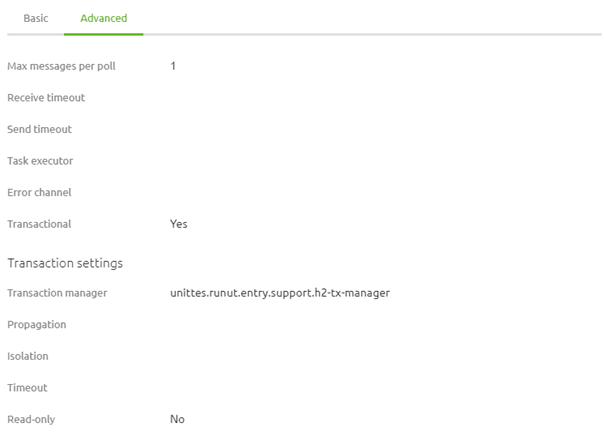
So what eMagiz gives you is a standardized database structure that temporarily stores messages (in case of connection issues). This is to ensure guaranteed delivery of the incoming message on the first queue in eMagiz (the onramp). As a bonus, the component helps you to smooth out the messages that are placed on the queue for further processing. With the help of this component, you prevent that when an external system offers 1000 messages within seconds all 1000 will end up on the queue at the same time. If that would happen you could run the risk of overloading your queue leading to larger issues (potentially even an 'out of memory' of the container).
Hopefully, this microlearning will give you some context on why the H2 database is automatically generated by eMagiz in every entry and plays a crucial role in holding up to the promise of delivering messages.
4. Key takeaways
- The H2 Database temporarily stores incoming data to ensure it is not lost if there are issues with the connection to the queue (the onramp).
- The H2 Database acts as an intermediary between the entry point where data arrives and the first queue, facilitating smooth data transfer.
- In case the queue cannot be reached, the H2 Database holds the data until the connection is restored, ensuring no data is lost.
- By periodically checking for new data, the H2 Database helps to regulate the flow of data from the connector to the container runtime, preventing overload and maintaining system performance.
- The component aids in managing message throughput to avoid overwhelming the queue, contributing to efficient and reliable message processing.
5. Suggested Additional Readings
If you are interested in this topic and want more information on it please read the release notes provided by eMagiz and see the following links:
