Configure A Backend Operation
In this microlearning, we will explore how to correctly configure backend operations within your API Gateway. Understanding how to properly set up these operations is crucial for effectively utilizing RESTful services and making these backend operations accessible through your API Gateway.
If you have any questions along the way, feel free to reach out to us at academy@emagiz.com.
1. Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of the eMagiz platform
2. Key concepts
This microlearning centers around configuring a backend operation with the API Gateway solution of eMagiz.
- With backend operation we mean: Any action that is available to be executed on an internal system that you want to make publicly available via the API Gateway.
- With API Gateway we mean: A collection of RESTful API operations that can be published to the outside world to give them access to applications that are linked to your business process.
When setting up your API Gateway integration the process of doing things is to start at the backend operation and based on that expose an operation in the API Gateway.
3. Configure a backend operation
The core concept of an API Gateway is to serve as an interface that centralizes and exposes backend operations to the outside world. It is then logical that, when you set up your API Gateway (i.e., the frontend facing part), you first start with the backend operation you want to expose.
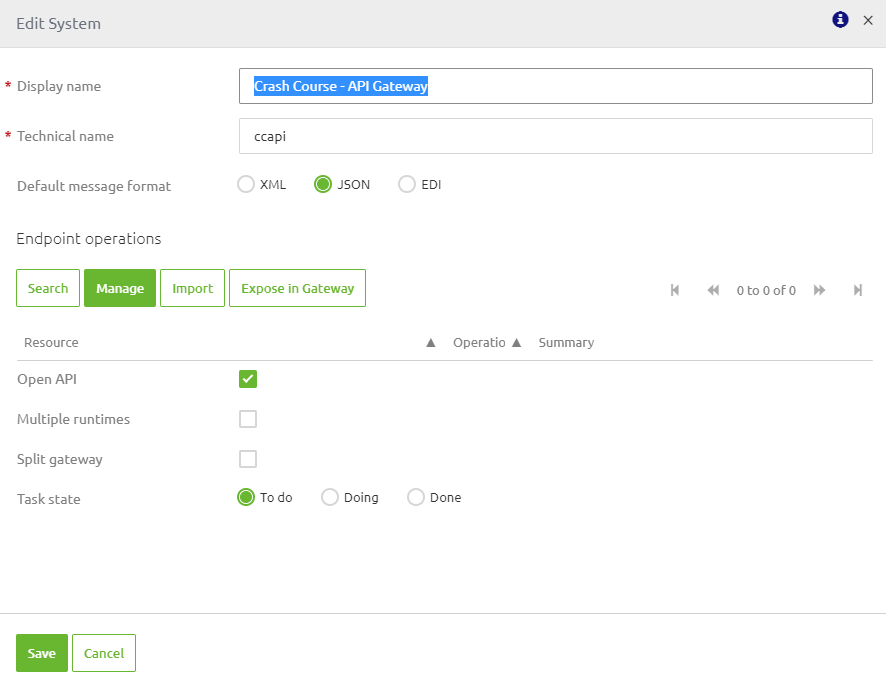
Configuring backend operations is done in the Design phase of eMagiz. When you are in the Design overview you can double click on the backend system that holds the operation(s). This action will show you the following pop-up:
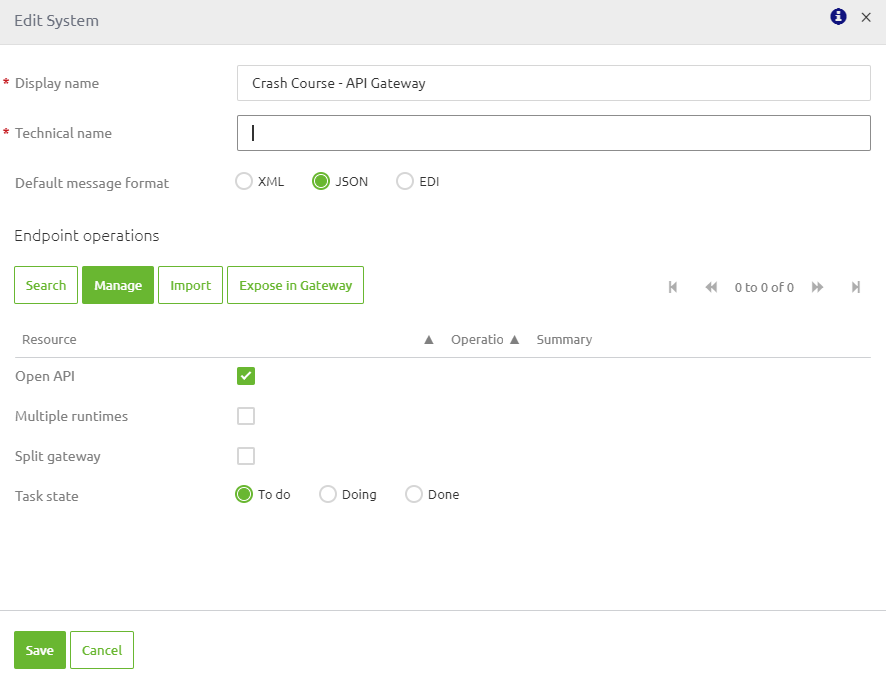
In here you need to fill in the technical name, just as with any other system. Furthermore, you have two decisions to make:
- Does the system talk JSON or XML (i.e., which message format)
- Can you specify the backend operations either via an import of the OpenAPI 3.0 spec or via a manual action
If the answer to the above decisions is JSON and yes the default settings are correct you should continue to either import the OpenAPI 3.0 spec or manually configure at least one backend operation.
More on that later in this microlearning.
In case the answer to the first decision is XML you should switch the default format to XML and unselect the OpenAPI 3.0 spec. The result should be something like this:
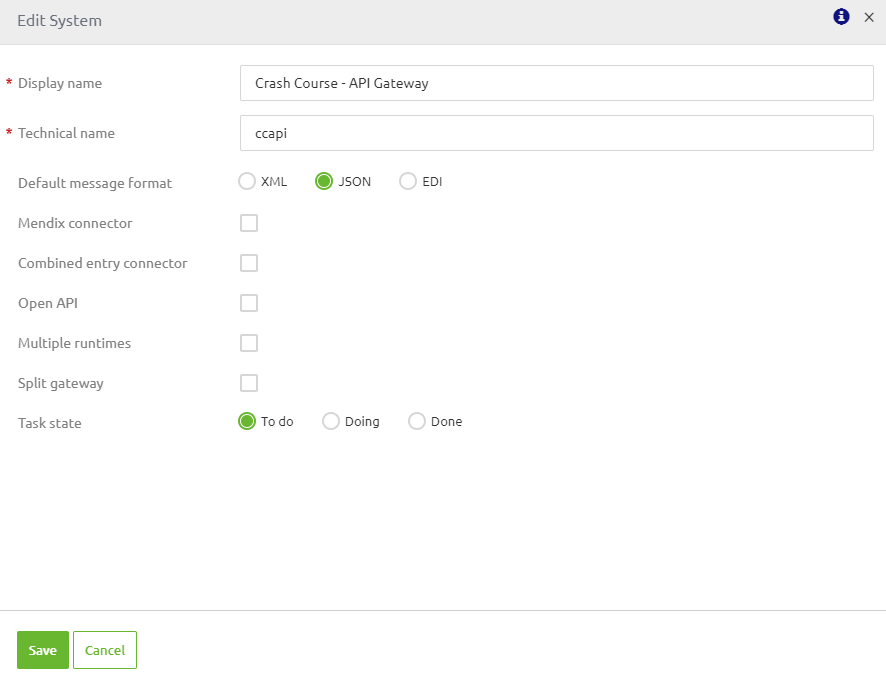
3.1 Importing a specification
If the external party can provide you with an OpenAPI 3.0 specification you can manage your backend system by pressing the Import button
when you are editing the system (double click on the system in question).
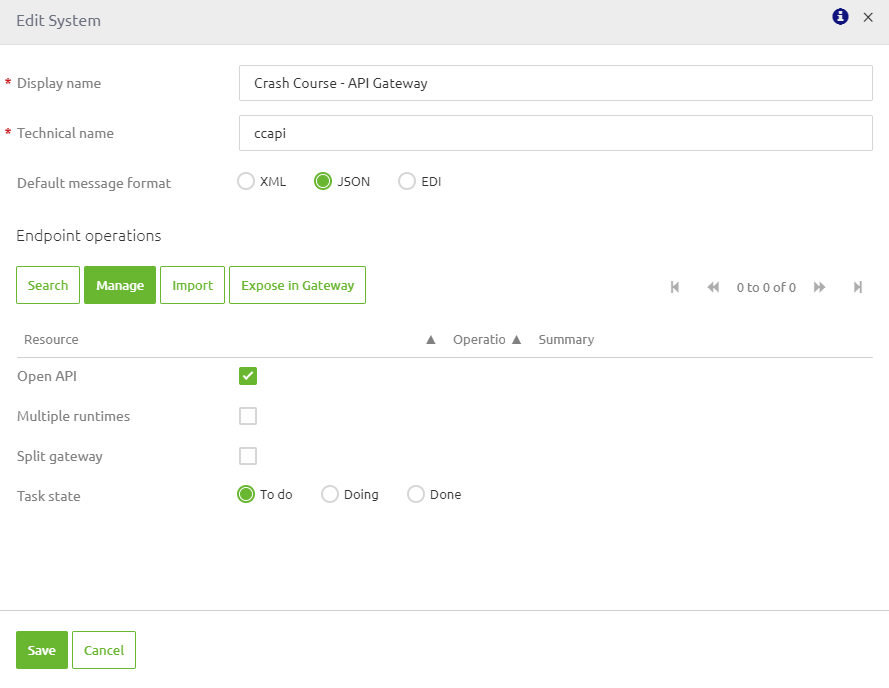
After you have pressed the Import button you enter the following pop-up. Here you can select the OpenAPI 3.0 JSON file to be imported in eMagiz.
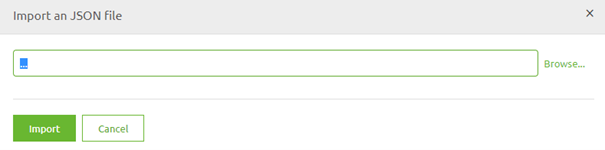
Press Import and let eMagiz do the heavy lifting for you. eMagiz will now import all backend operations that are specified in the OpenAPI 3.0 JSON file you have selected.
A result of such an import could be as follows:
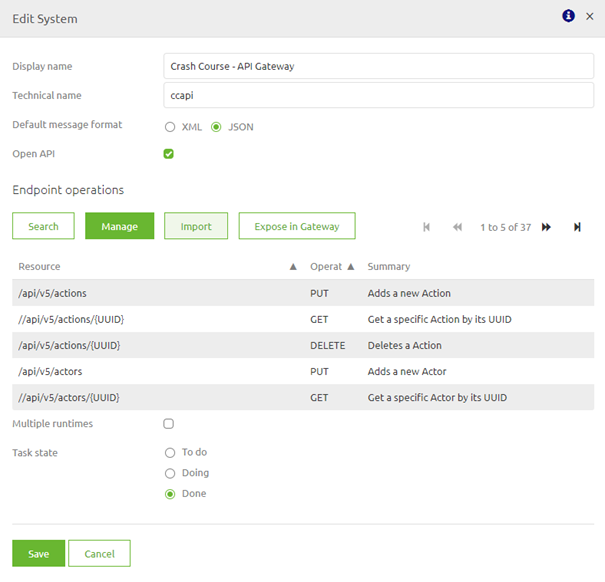
Congratulations you have successfully imported your OpenAPI 3.0 specification.
3.2 Creating a specification
It can very well be that the external party has a swagger definition, but not an OpenAPI 3.0 standard.
Or maybe they have other documentation that tells you the resource paths, parameters, and HTTP operations that you need.
In all these cases you can manage your backend system by pressing the Manage button when you are editing the system (double click on the system in question).

When you select the option Manage you will be presented with the following pop-up. The first time this pop-up will be empty. All other times it should contain at least one backend operation.
Let us manually fill a simple GET call to retrieve all HTTP methods. So, we start at the top left of the screen in the resource section and press New.
In the pop-up that follows, we enter the resource path that is defined in the specification and press Save. The result will be as follows:

The next step will be to add an operation via the option New under Operations in the middle of your screen. The result of that action will be something as follows:
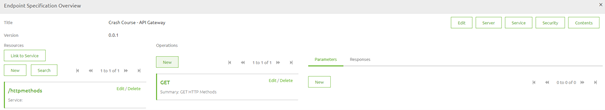
As there are no parameters in this case you have now successfully configured your first backend operation. When you close this screen you will see the results on system level.
Now you can Save or add another operation to add to your specification.
3.3 Next steps
After you have correctly configured your backend operation you can start to think about how you can best expose the operations via the API Gateway.
In the next three microlearnings, we will delve deeper into the various components and also learn how you can quickly expose these backend operations in your API Gateway.
4. Key takeaways
- The starting point of setting up your API Gateway is configuring the backend operation(s)
- There are two ways to do so for JSON based systems
- Import OpenAPI 3.0 specification
- Manually configure based on other specification
- Other cases such as connecting to XML based systems will be discussed later on
5. Suggested Additional Readings
If you are interested in this topic and want more information on it please read the help text provided by eMagiz and read the following links:
