Security
In this microlearning, we will explore the essential steps to securing your API Gateway. In today’s digital landscape, protecting your APIs is crucial to ensuring that only authorized users can access your services. We will begin by covering general security measures to verify client identities and introduce the built-in options eMagiz provides for safeguarding your API Gateway. In the following microlearning, we will delve deeper into configuring roles and user permissions to ensure robust protection for your API operations.
If you have any questions along the way, feel free to reach out to us at academy@emagiz.com.
1. Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of the eMagiz platform
2. Key concepts
This microlearning centers around securing the API Gateway in general.
- With securing we mean: Configuring a method that will be used to validate that the clients are who they say they are
- With API Gateway we mean: A collection of RESTful API operations that can be published to the outside world to give them access to applications that are linked to your business process
3. Security
While "security" is a broad term, this microlearning focuses specifically on the general security measures that ensure clients can prove their identity to the API Gateway, i.e., how clients should prove to the API Gateway that they are who they say they are. We will then explore the methods eMagiz provides to verify client authenticity.
When you want to set up your security in combination with the eMagiz API Gateway we offer three options out of the box:
- API Key
- OpenID Connect
- OAuth 2.0
All three methods can be supplemented with the requirement that a client needs to send along a client certificate when executing the call.
To choose the security measure for your API Gateway you can navigate to Design and open the context menu on API level (the API segment in the middle of the Design overview)
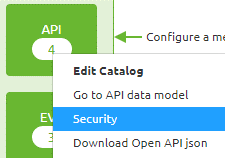
Choosing this option will lead you to the following screen. Here you can add a New security scheme or edit the existing one.
Take into account that you should select one security scheme that is in place for all your environments.
Below we will talk about each of these three options.
3.1 API Key
The simplest form of authentication is with the help of a so-called API Key.
This is the most low-level solution available in terms of authorization.
In this case, the client will send a specific key that they have received from us in a certain header and we will check if the value is correct.
If not the client will receive a 401 Unauthorized
Best practice is to name the header x-api-key. A example of how you can configure this is:
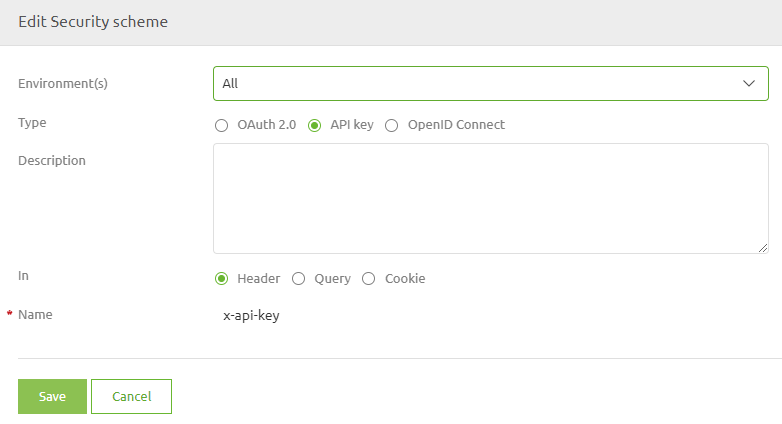
This method is frequently used in a situation that demands less technical complexity and deals with less sensitive data.
An eMagiz best practice is to always combine this option with the use of a client certificate whenever possible.
3.2 OpenID Connect
Both OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0 work with an authorization server. On this server it is specified if you have rights and if so to what exactly.
To authenticate themselves they first have to send a request to the authorization server. In all subsequent calls, they will have to use the information in the bearer to authenticate themselves.
As you can see this becomes a lot more complex to implement for an outside party. On the flip side, it is a lot better in terms of security.
When using the IDP provided within the platform you can leave the configuration as it is configured for you on default when you select this option for implementing your eMagiz API Gateway solution.
To configure this option simply configure the security scheme as follows:
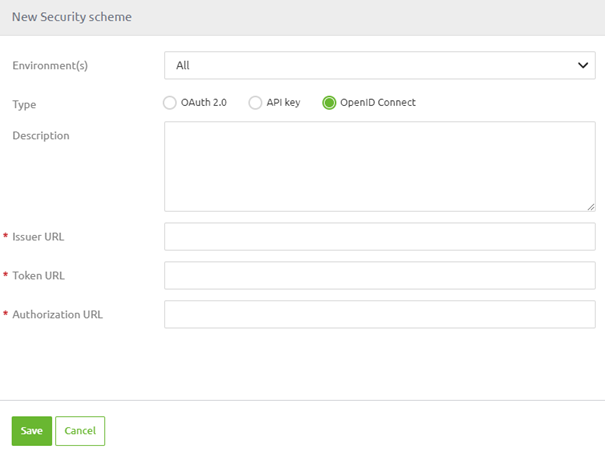
3.3 OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials
As said OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0 are very similar solutions. Only not all OAuth 2.0 providers accept OpenID connect. Another reason to not use the authorization server that eMagiz can provide you is the fact you already have your authorization server (i.e. Azure AD) in which you already manage this.
For cases that are covered by either of those reasons, we offer the OAuth 2.0 option. When using the IDP provided within the platform you can leave the configuration as it is configured for you on default when you select this option.
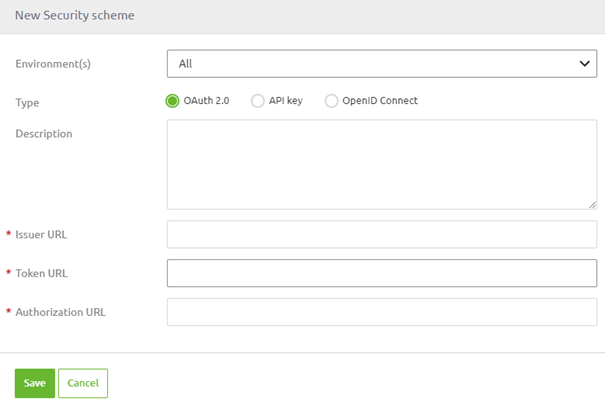
3.4 OAuth 2.0 Authorization code
One can also choose to use the grant type Authorization code as part of OAuth 2.0 security as described in the previous paragraph. When chosing OAuth 2.0 as the security mechanism of choice for your API Gateway the default grant type is the 'Client Credentials' grant type. However, we have functionality that allows you to deviate from this standard on a system by system basis. You can change this selection by editing the system configuration in Design. Once the 'Authorization code' grant type has been selected as one can see below, the specific call-back URLs (comma separated list) need to provided to support the login process that comes with this grant type.
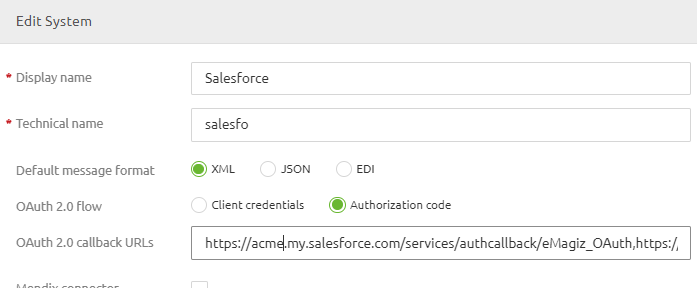
Once this is done, the first time the requesting application will need the provided username and password to login to our IDP Server. This is usually an object inside the application requestor. This username and password will be generated by our IDP server. Once done the configuration will work like the grant type client credentials.
Note that to test this security configuration via the Swagger UI sections of eMagiz, the same two-step approach is needed to test and validate the operation to which the system has been granted access to.
4. Key takeaways
- Security encompasses various aspects, and in this session we focused on how to verify client identities to ensure authorized access.
- eMagiz offers three key methods for securing your API Gateway:
- API Key: A basic form of authentication using a unique key.
- OpenID Connect: A more advanced method leveraging an authorization server for authentication.
- OAuth 2.0: A flexible option that can be tailored to use different grant types, including Client Credentials and Authorization Code.
- In the next microlearning, we will cover how to configure roles and permissions to further control access to your API operations.
5. Suggested Additional Readings
If you are interested in this topic and want more information on it please read the help text provided by eMagiz and the following link.
