Install Docker for Windows
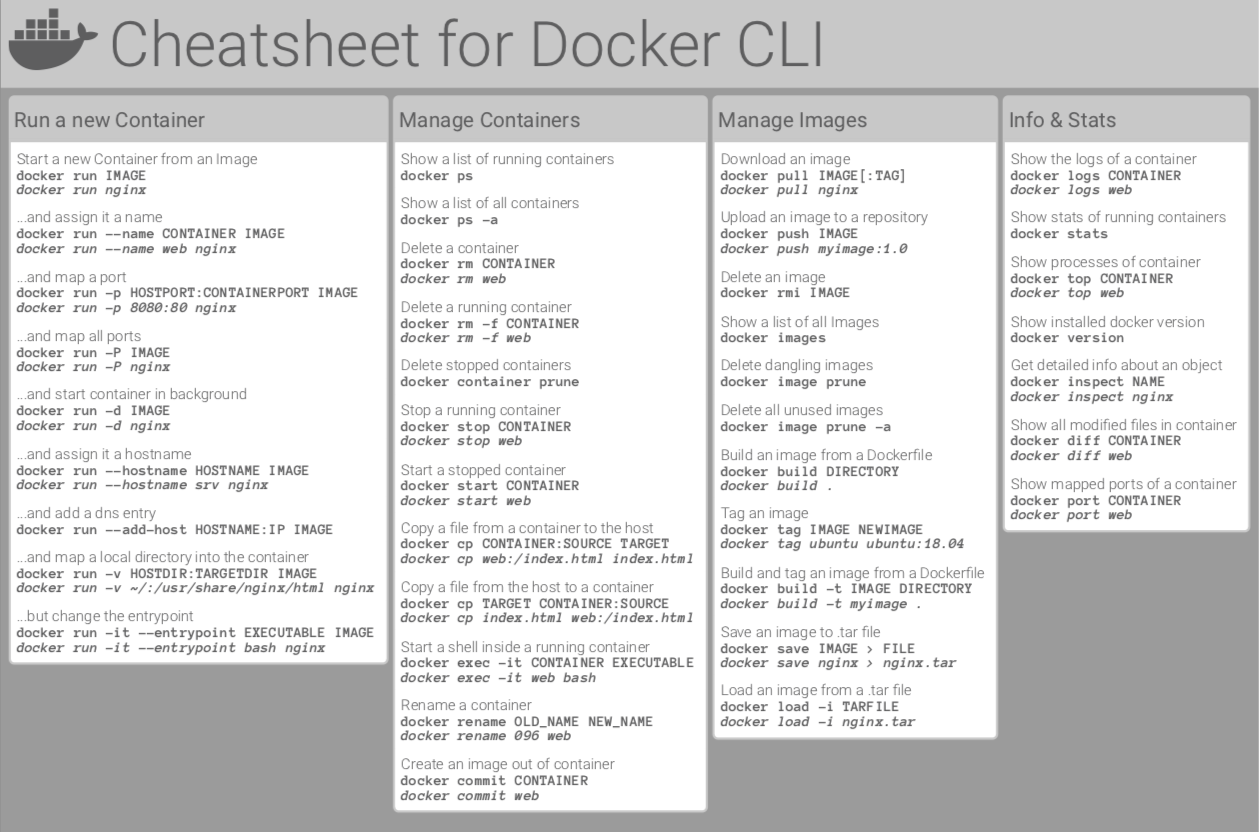
In eMagiz's current runtime architecture, Docker technology is utilized to deploy runtimes efficiently. eMagiz provides specific runtime images that can be deployed within dockerized environments. This section outlines the steps needed to prepare a Windows server for the installation of the eMagiz Deploy Agent, which is responsible for downloading these images from the eMagiz infrastructure.
Should you have any questions, please contact academy@emagiz.com.
1. Prerequisites
- Advanced knowledge of the eMagiz platform
- Good understanding of eMagiz runtimes in general
2. Key concepts
In the current runtime architecture of eMagiz, Docker technology is used to deploy runtimes. eMagiz creates specific runtime images that contain the eMagiz runtime, and can be deployed in dockerized environments.
In the below section the Windows variant is described in terms of how to prepare the server to allow the eMagiz Deploy Agent to be installed. That agent allows to download images from the eMagiz infrastructure.
3. On-premises deployments
3.1 General requirements
3.2 Installation Windows
Whenever Windows is selected as operating system, you need to have a Windows Server 2022 version. Older Windows servers are not supported.
3.2.1 Docker Installation
To install or update docker on your machine, execute the following commands in powershell with administrative rights:
.\install-update-docker-ce.ps1 -DockerVersion DESIRED_VERSION
3.2.2 Customization
After installing Docker you have the option to stick with the standard configuration of Docker or you can opt to alter some specific settings. Settings that can be of particular interest are the setting that defines the IP address range your Docker installation will use to run the containers and the setting that defines where to store data (i.e. containers and images). To check the full list of compatible configuration options for Windows you can check: Configure Docker in Windows.
3.2.2.1 IP address range
Below you can find the code necessary to configure a different IP address range.
#Add following lines
{"fixed-cidr": "<ip-address>"}
3.2.2.2 Data location
Below you can find an example of switching from the default C directory (c:\programdata\docker) to the D directory to store data related to Docker. Based on your internal configuration you can choose the best suitable variant if that is needed. To do so you can add the following attribute to the Docker daemon file:
#Add following lines
{
"data-root": "d:\\docker"
}
3.2.3 Check installation
After executing the commands above, the server will restart if required. After the restart, execute the following command
If the command returns that the command cannot be found, please run the following command again.
3.2.3 Verify docker functionality
Execute the following command
The result of this call should show the following:
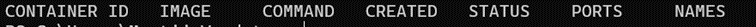
3.2.4 Install eMagiz Deploy Agent
Install the eMagiz Deploy agent as can be found in this microlearning
3.3 Uninstall Docker
To uninstall docker from your machine, execute the following commands in powershell with administrative rights:
Example usage:
4. Key takeaways
- eMagiz uses runtime images to deploy emagiz runtime on dockerized environments. The runtime image holds all the information and components required to run the runtime
- eMagiz has a specific agent that manages the download of that image to the on-premises server
- The firewall of the on-premises environment should allow outgoing traffic without any restriction. In case that is not desirable, eMagiz can provide the addresses and ports needed to setup the right firewall rules.