Design an Event Processor
In this microlearning, we will dive into designing an event processor in eMagiz. An event processor helps you to transport, filter, and transform data between topics. We will cover the essentials, from prerequisites to the actual design process, to help you set up your event processor effectively.
Should you have any questions, please contact academy@emagiz.com.
1. Prerequisites
- Intermediate knowledge of the eMagiz platform
- An Event Streaming License
- Knowledge of the Event Streaming Pattern
- Followed the crash course on Event Streaming
2. Key concepts
This microlearning centers around designing an event processor.
- By event processor, we mean: A flow within eMagiz that consumes data from one topic and transports the data to another topic. In between, you have the option to filter or transform the data (i.e., event)
To create an event processor we need the following:
- An input topic designed in eMagiz.
- An output topic designed in eMagiz.
3. Design an Event Processor
An Event processor is a flow within eMagiz that retrieves data from one topic (the so-called input topic) and transports the data to another topic (the so-called output topic). During the transport of the data, you can transform the event or filter out events that don't fit your criteria.
In this microlearning, we will learn how you can design your event processor. In the microlearnings that will follow we will build on this knowledge.
3.1 Input and Output Topic
The first step of setting up your event processor is determining which topics you want to transport the data to. An Event processor needs an input and an output topic to function correctly. When you have established what the input and output topic is you can determine whether these topics are already designed in eMagiz.
In this microlearning, we assume that the topics are already exists. Please refer to this and this microlearning for more information on how to create topics in your model.

Since we already have the input and output topics we can move to the Design phase of eMagiz. In this phase, you can design the event processor.
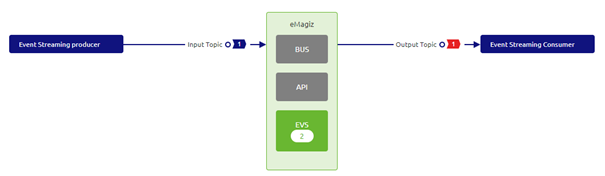
3.2 Link Input to Output via an Event Processor
As you can see in this picture (and probably remember from one of our earlier microlearnings) there are no systems that produce data on the Output topic.
This is where eMagiz comes in. Via the event processor, you can configure that all data from the Input topic will be transported towards the output topic. In other words, eMagiz will become the producer of data on the Output topic.
To design an event processor you simply navigate to one of the lines drawn that represent the input and the output topic and access the context menu via a right-mouse click.

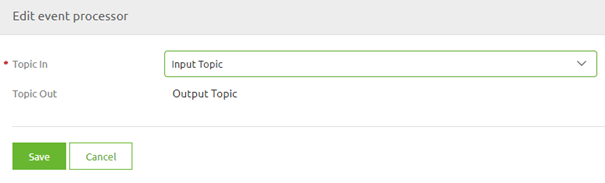
When you select the option called Add processor you will see a pop-up similar to the one shown below. Do notice that depending via which line you access the context menu what can be altered changes. When you select the line that has a consuming system you can select the input topic. When you select the line that has a producing system you can select the output topic.

Select the correct topic and press Save.
As a result, your Design overview will change to reflect the choices that you have made
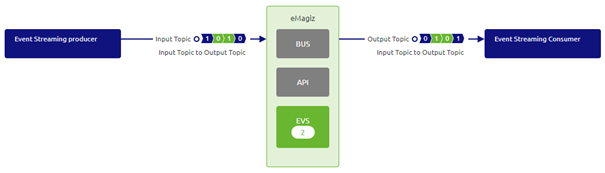
You have now successfully designed an event processor that is capable of transporting data from the Input Topic to the Output Topic.
3.3 Double Lane Consideration
When running your Event Streaming processor(s) in a double lane setup you should be aware that both consumers will become part of the same consumer group and therefore the minimum number of partitions on the topics read by the event processor should be two. For an explanation on how consumers groups work please see this fundamental page.
4. Key takeaways
- An event processor facilitates the movement of data from an input topic to an output topic, enabling both the transport and transformation of data.
- In eMagiz, designing an event processor involves selecting the appropriate input and output topics and configuring the processor to manage data flow between them.
- In an event processor flow, you have the option to filter or transform events according to your criteria.
- Ensure your topics are properly set up before design. If running multiple processors, be aware of consumer group settings and partition requirements for optimal performance.
5. Suggested Additional Readings
If you are interested in this topic and want more information on it please read the release notes provided by eMagiz that accompany the eMagiz Mendix Connector version you have selected and read the following link:
